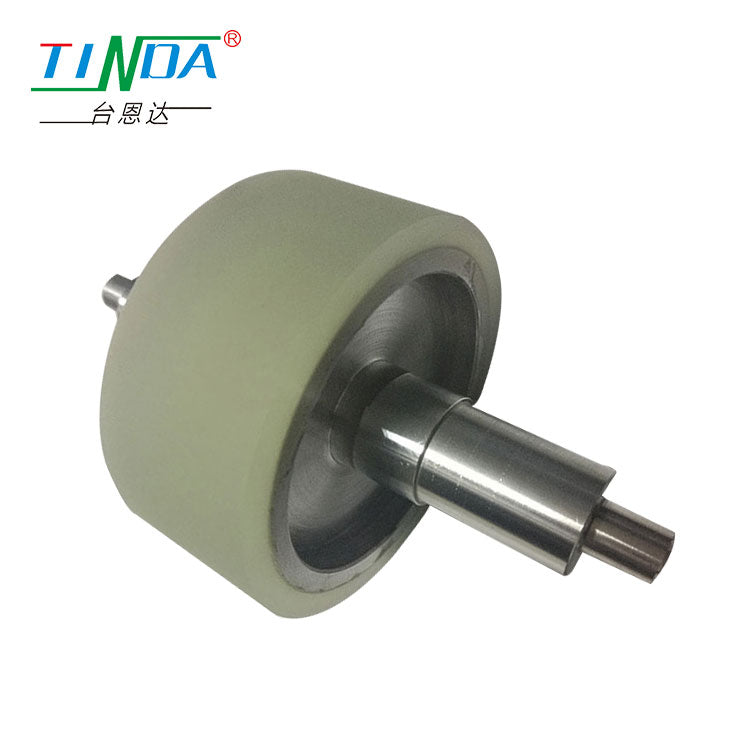
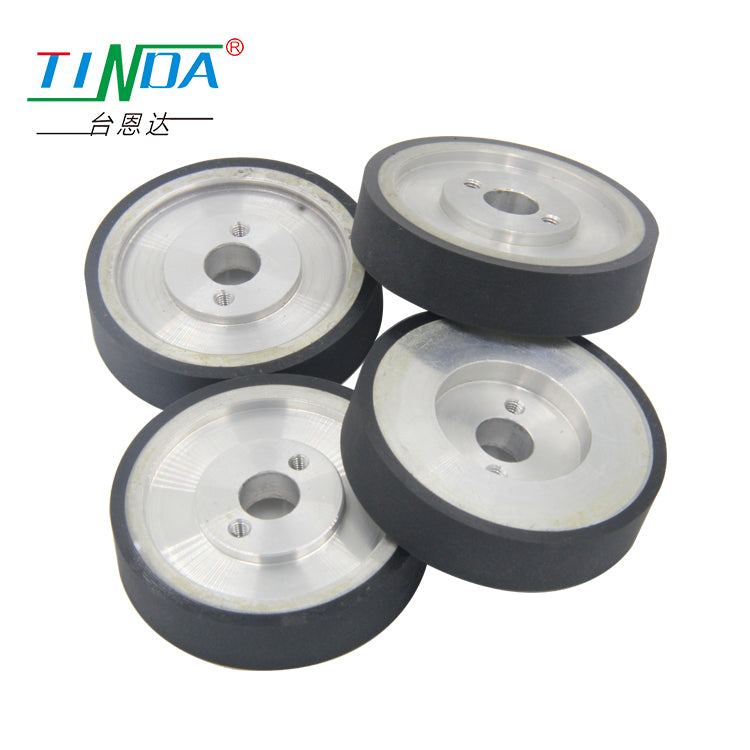
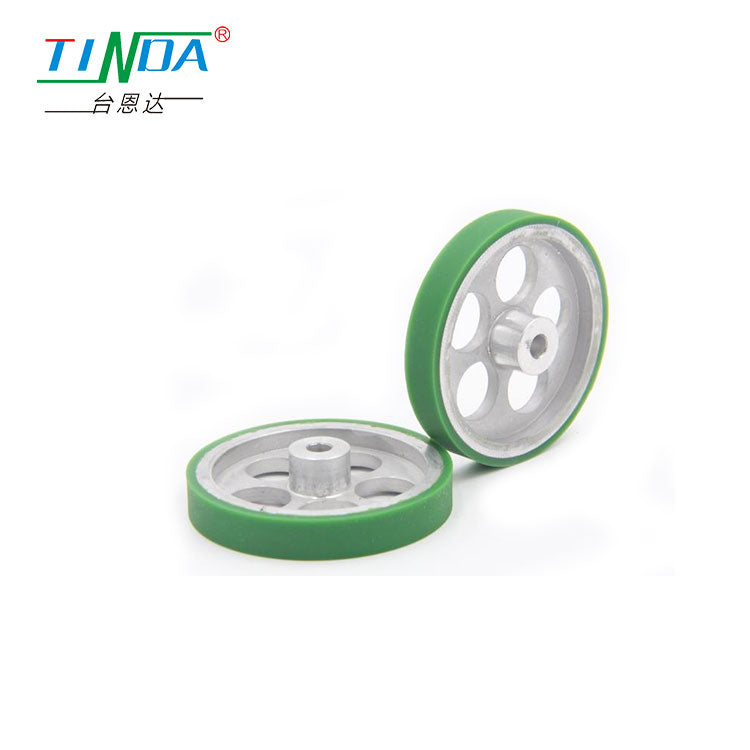

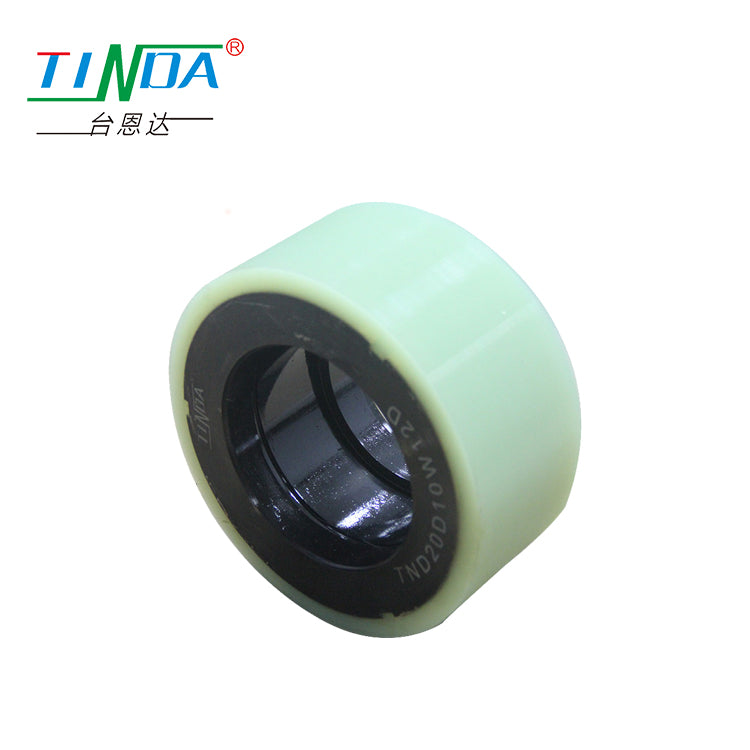

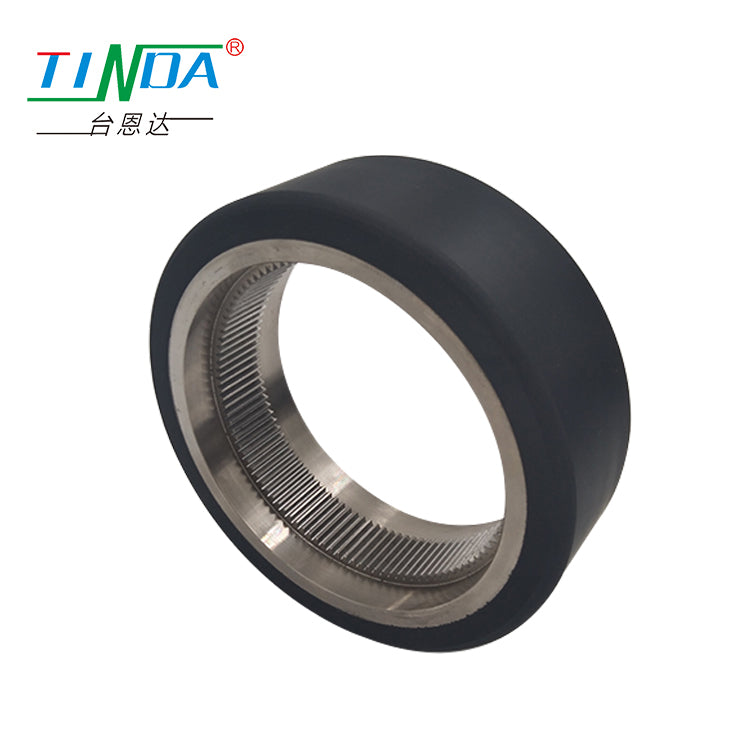





AGV/AMR drive wheel
Product feature:It has the characteristics of high load, low noise, wear and shock absorption, corrosion resistance, ultraviolet resistance, small resistance and no deformation.
Application: Widely used in food processing, factory handling, warehousing and logistics, AGV/AMR robots and other industries.

| KEYWAY | STRAIGHT AFTER THE | WHEEl WIDTH | BEARING | HARDNESS | WHEEL MATERIAL | THE WHEEL CORE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Φ25 | 165MM | 40MM | 420KG | 80A | polyurethane(PU) | steel core |

AGV/AMR driven wheel
Product feature: load, low noise, wear and shock absorption, corrosion resistance, UV resistance, small resistance and deformation.
Application: It is widely used in food processing, factory handling, warehousing and logistics, AGV/AMR robots and other industries.n.

| THE FLANGE | STRAIGHT AFTER THE | WHEEl WIDTH | BEARING | HARDNESS | WHEEL MATERIAL | THE WHEEL CORE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| flange | 165MM | 40MM | 450KG | 75A | polyurethane(PU) | aluminium alloy |

AGV/AMR steering wheel
Product feature: size, integrated design, small size, light weight. Simple operation, integrated automatic center function, strong adaptability, various forms,Drive plus steering system.
Application: Can quickly deploy AGV/AMR, mobile robots, etc. It perfectly meets the application requirements of AGV/AMR

| flange | TYPE | DC | actuating motor |
| VOLTACE POWER | W | 400 | |
| ELECTRIC POWER VOLTAGE | V | 48 | |
| ELECTRIC POWER VOLTAGE | V | 300 | |
| ELECTRIC SPEED | Rpm | 3000 | |
| ELECTRIC ELECTRIC CURRENT | A | 10.1 | |
| RATED TORQUE | Nm | 1.27 | |
| LEVEL OF PROTECTION | IP | 65 | |
| ENCODER | Magnetic braiding | increment | |
| ENCODER | resolution ratio | 1024 |
| PARAMETERS OF THE TRACTOR |
TYPE | X | Row speed reducer | |
| SPEED RATIO OF REDUCER | i | 20 | 68 | |
| REDUCER TORQUE | Nm | 100 | 120 | |
| POLYURETHANE LOAD BEARING | Kg | 1000 | 1000 | |
| RUBBER LOAD BEARING | Kg | 900 | 900 | |
| BRAKE TORQUE | Nm | 76 | 358.4 | |
| BRAKE VOLTAGE | V | DC24 | DC24 | |
| MAXIMUM SPEED | M/min | 70.7 | 20.8 | |
| TRACTION | N | 322 | 1036.3 | |
| WEIGHT OF TRACTION | reference | 547 | 1658 | |
| STEERING MOTORPA RAMETERS |
TYPE | DC | servo motor |
| MOTOR POWER | W | 200 | |
| MOTOR VOLTAGE | V | 48 | |
| MOTOR SPEED | Rpm | 3000 | |
| CURRENT OF MOTOR | A | 5.1 | |
| SPEED RATIO OF REDUCER | i | 35+(105: 30) | |
| REDUCER TORQUE | Nm | 35 | |
| LEVEL OF PROTECTION | IP | 65 | |
| ENCODER | Magnetic braiding | increment | |
| ENCODER | resolution ratio | 1024 | |
| LEFT AND RIGHT LIMIT | Io | Normally open, normally closed | |
| MAXIMUM DEGREE OFSTEERING | ± | 140° |

Macnum wheel
Product feature:The McNum wheel has compactstructure and flexible movement, which is verysuitable for the working environment withnarrow and limited space and more right Angleoends
Application: lt is applied to the precision dockingassembly, transportation, and maintenance of so-phisticated machinery and equipment oflargeobjects, such as the maintenance of aerospaceand aviation, and the logistics and handling ofenterprises and factories.

| McNum parameter table | ||||
| DIAMETER OF TIRE | 60mm | 75mm | 100mm | 127mm |
| WEIGHT (SET OF 4) | 0.35kg | 0.45kg | 1.55kg | 2.0kg |
| LOAD CAPACITY (4 LOADS) | 15kg | 15kg | 45kg | 70kg |
| THICKNESS(EXCLUDING COUPLING) | 32mm | 32mm | 51mm | 51mm |
| DIAMETER OF SUPPORTING WHEEL | 3mm | 3mm | 4mm | 4mm |
| NUMBER OF SUPPORTING WHEELS | 8 | 10 | 9 | 12 |
| OUTPUT SHAFT DIAMETER | 4、5、6、8mm | 6、8、10、12、14、15、16mm | ||
| SURFACE TECHNICS | Aluminum alloy, surface sandblasting process | |||

| PROJECT | TRADITIONAL AGV | MCKNUM WHELL OMV |
| Driving wheel form | Usually polyurethane wheels are used | The McKnum wheel |
| Number of driving wheels | 2 PCS | 4 PCS |
| Number of driving wheel components | 2 Groups | 4 Groups |
| Motor direction | Forward. back turn | Forward, backward, left and right transverse movement, zero turning radius, oblique line in any direction, etc |
| Space usage | Big | Small |
| Flexibility of movement | Low | High |
| Cost | Low | Higher |
| Control system | Simpleness | Complex |
| Structural style | Simpleness | Complex |
| Manufacturing requirements | Ordinary | Higher |
| Multi-ground environmental requirements | Higher | High |












